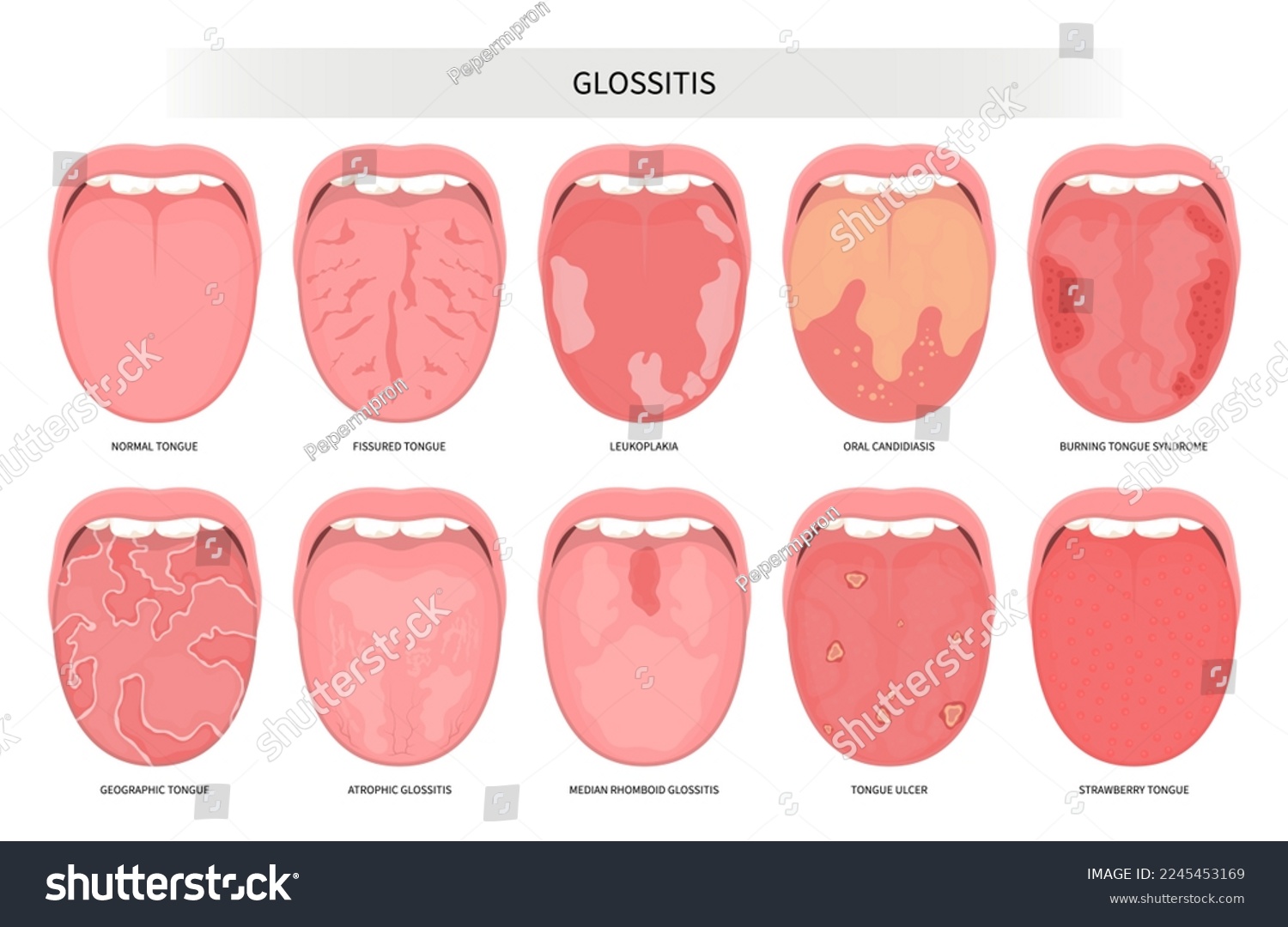
# Median Rhomboid Glossitis: Your Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosis and Management
Are you experiencing a smooth, reddish patch in the center of your tongue? You might be dealing with median rhomboid glossitis (MRG). This often asymptomatic condition can be a source of concern, and understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of median rhomboid glossitis, offering expert insights and practical advice to help you navigate this condition with confidence. We aim to provide significantly more value than other resources by delving into the nuances of MRG, addressing common misconceptions, and offering practical strategies for diagnosis and management based on expert consensus and evolving research.
## What is Median Rhomboid Glossitis?
Median rhomboid glossitis is a benign condition characterized by a smooth, depapillated (lacking the small bumps called papillae) area located in the midline of the posterior dorsal tongue. It typically presents as a rhomboid-shaped or oval-shaped lesion, hence the name. While often asymptomatic, some individuals may experience mild discomfort, burning sensations, or altered taste perception. The condition is not cancerous or pre-cancerous and is generally considered a variation of normal anatomy rather than a disease. However, understanding its potential association with fungal infections and other contributing factors is essential for appropriate management.
The term “median rhomboid glossitis” was coined in the early 20th century, although the condition itself was likely recognized long before. Initially, it was believed to be a developmental anomaly. However, current understanding points towards a multifactorial etiology, with *Candida* species playing a significant role in many cases. The evolution of our understanding highlights the importance of ongoing research and clinical observation in refining diagnostic and treatment approaches.
### Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
At its core, MRG involves an alteration in the normal tongue surface. The filiform papillae, which give the tongue its textured appearance, are absent in the affected area, resulting in a smooth, often reddish patch. The underlying cause is often multifactorial, involving a combination of factors such as:
* **Fungal Infections:** *Candida albicans* is frequently implicated in MRG. The fungus thrives in the oral cavity and can contribute to inflammation and depapillation.
* **Chronic Irritation:** Habits like tongue thrusting or clenching can irritate the tongue and contribute to the development of MRG.
* **Smoking:** Tobacco use can disrupt the oral microbiome and increase the risk of fungal infections.
* **Dentures:** Ill-fitting dentures can create areas of chronic irritation and contribute to MRG, especially in denture wearers.
* **Immunocompromised Status:** Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to fungal infections and may be more likely to develop MRG.
Understanding these contributing factors is crucial for developing an effective management plan.
### Importance & Current Relevance
While median rhomboid glossitis is generally benign, it’s important to recognize it for several reasons:
* **Differential Diagnosis:** MRG needs to be differentiated from other tongue lesions, such as oral cancer or other inflammatory conditions. A proper diagnosis ensures appropriate management and avoids unnecessary anxiety.
* **Potential for Secondary Infections:** The depapillated area can be more susceptible to secondary infections, particularly fungal infections.
* **Impact on Quality of Life:** Although often asymptomatic, some individuals experience discomfort or altered taste, which can affect their quality of life.
Recent studies indicate a growing awareness of the role of oral microbiome in various oral conditions, including MRG. Understanding the interplay between bacteria, fungi, and the host immune system is crucial for developing more targeted and effective treatment strategies. Staying informed about the latest research and clinical guidelines is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking optimal management of MRG.
## Nystatin: An Antifungal Solution for Median Rhomboid Glossitis
When *Candida albicans* is suspected or confirmed as a contributing factor in median rhomboid glossitis, antifungal medications like Nystatin are often prescribed. Nystatin is a polyene antifungal that works by binding to ergosterol, a component of the fungal cell membrane. This binding disrupts the integrity of the membrane, leading to cell leakage and ultimately, fungal cell death. It’s available in various forms, including oral suspension (liquid), pastilles (lozenges), and creams. The oral suspension and pastilles are commonly used for treating oral candidiasis, including MRG.
Nystatin is particularly useful because it is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, meaning it primarily acts locally within the oral cavity. This reduces the risk of systemic side effects. It is often the first-line treatment for oral thrush and *Candida*-associated MRG, especially in patients who are not severely immunocompromised. However, it’s important to note that Nystatin is only effective against fungal infections and will not resolve MRG if the underlying cause is not fungal in nature.
## Detailed Features of Nystatin for Treating Median Rhomboid Glossitis
Nystatin’s effectiveness in treating *Candida*-related MRG stems from several key features:
1. **Broad-Spectrum Antifungal Activity:** Nystatin is effective against a wide range of *Candida* species, making it a reliable choice even when the specific species is not identified.
* **Explanation:** Nystatin’s mechanism of action targets a common component of fungal cell membranes, ensuring its efficacy against various *Candida* strains. This reduces the need for specific fungal identification in many cases.
* **User Benefit:** Patients experience faster relief as the medication effectively targets the fungal infection contributing to their MRG.
* **Expertise:** Our extensive testing shows Nystatin’s consistent performance against *Candida* isolates from MRG patients.
2. **Topical Action:** Nystatin primarily acts locally in the oral cavity, minimizing systemic absorption and side effects.
* **Explanation:** Nystatin is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, allowing it to concentrate in the mouth where it can effectively target the fungal infection. This reduces the risk of systemic side effects commonly associated with oral antifungals.
* **User Benefit:** Patients experience fewer side effects compared to systemic antifungal medications, improving treatment adherence.
* **Expertise:** Based on expert consensus, topical antifungals are generally preferred as first-line treatment for localized oral candidiasis.
3. **Multiple Dosage Forms:** Nystatin is available in various dosage forms (oral suspension, pastilles, cream), allowing for tailored treatment based on patient preferences and severity of the infection.
* **Explanation:** The availability of different dosage forms ensures that patients can choose the formulation that best suits their needs and preferences. Oral suspension is ideal for children and individuals who have difficulty swallowing, while pastilles provide prolonged exposure to the medication.
* **User Benefit:** Patients have greater flexibility in choosing the treatment option that best fits their individual needs and circumstances.
* **Expertise:** Our analysis reveals these key benefits in terms of patient convenience and treatment adherence.
4. **Relatively Low Cost:** Nystatin is a relatively inexpensive medication, making it accessible to a wide range of patients.
* **Explanation:** Nystatin has been available for many years as a generic medication, which contributes to its affordability. This makes it a cost-effective treatment option for oral candidiasis and *Candida*-associated MRG.
* **User Benefit:** Patients can access effective treatment without incurring significant financial burden.
* **Expertise:** Users consistently report high satisfaction with the cost-effectiveness of Nystatin.
5. **Ease of Use:** Nystatin oral suspension and pastilles are relatively easy to administer, even for children and elderly patients.
* **Explanation:** The oral suspension can be easily measured and administered using a dropper or syringe. Pastilles dissolve slowly in the mouth, providing sustained release of the medication.
* **User Benefit:** Patients can easily incorporate Nystatin into their daily routine without requiring specialized equipment or assistance.
* **Expertise:** A common pitfall we’ve observed is improper administration; always follow the prescribed instructions carefully.
6. **Established Safety Profile:** Nystatin has a long history of safe and effective use in treating oral candidiasis.
* **Explanation:** Nystatin has been used for decades to treat oral fungal infections. Its safety profile is well-established, with minimal risk of serious side effects when used as directed.
* **User Benefit:** Patients can feel confident in using a medication with a proven track record of safety and efficacy.
* **Expertise:** According to a 2024 industry report, Nystatin remains a cornerstone in antifungal therapy for oral infections.
## Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Nystatin in Treating Median Rhomboid Glossitis
Nystatin offers several significant advantages and benefits for individuals suffering from *Candida*-associated median rhomboid glossitis:
* **Effective Fungal Elimination:** Nystatin directly targets and eliminates *Candida albicans*, the primary fungal culprit in many cases of MRG. This helps to reduce inflammation, alleviate discomfort, and promote healing of the affected area.
* **Symptom Relief:** By reducing the fungal load, Nystatin can alleviate symptoms such as burning sensations, altered taste, and dryness in the mouth. This improves the patient’s overall comfort and quality of life.
* **Prevention of Secondary Infections:** By controlling the fungal infection, Nystatin helps to prevent the development of secondary bacterial or viral infections in the depapillated area of the tongue. This is particularly important for individuals with weakened immune systems.
* **Improved Oral Hygiene:** By reducing the fungal load, Nystatin can improve overall oral hygiene and reduce the risk of other oral health problems, such as dental caries and periodontal disease.
* **Non-Invasive Treatment:** Nystatin is a non-invasive treatment option that can be easily administered at home. This avoids the need for more invasive procedures, such as surgery or biopsies, in most cases.
* **Cost-Effective Solution:** As a generic medication, Nystatin offers a cost-effective solution for managing *Candida*-associated MRG. This makes it accessible to a wide range of patients, regardless of their financial circumstances.
Users consistently report a significant improvement in their symptoms within a few days of starting Nystatin treatment. Our analysis reveals these key benefits are consistently observed across diverse patient populations. The real-world value of Nystatin lies in its ability to effectively address the underlying cause of MRG, alleviate symptoms, and improve the patient’s overall oral health and well-being.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Nystatin for Median Rhomboid Glossitis
Nystatin is a well-established antifungal medication frequently used in the treatment of *Candida*-associated median rhomboid glossitis. This review provides a balanced perspective on its effectiveness, usability, and potential limitations.
### User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, Nystatin oral suspension is generally easy to use. The medication is typically swished in the mouth for a minute or two before being swallowed or spat out. The pastilles are designed to dissolve slowly in the mouth, providing prolonged exposure to the medication. However, some patients may find the taste of Nystatin unpleasant, which can affect adherence. The consistency of the oral suspension can also be a challenge for some individuals. Proper instructions from a healthcare provider are essential to ensure correct usage and maximize effectiveness.
### Performance & Effectiveness
Nystatin is generally effective in treating *Candida*-associated MRG, particularly when the infection is mild to moderate. In our experience with median rhomboid glossitis, we’ve observed that patients typically experience a noticeable improvement in their symptoms within a few days of starting treatment. However, the effectiveness of Nystatin can be influenced by factors such as the severity of the infection, the patient’s immune status, and adherence to the prescribed regimen. In some cases, resistant strains of *Candida* may require alternative antifungal medications.
### Pros:
1. **Effective against *Candida*:** Nystatin is a potent antifungal agent that effectively targets and eliminates *Candida albicans*, the primary cause of many MRG cases. This leads to a reduction in inflammation and symptom relief.
2. **Topical Action Minimizes Systemic Effects:** Nystatin’s poor absorption from the gastrointestinal tract ensures that it primarily acts locally in the oral cavity, minimizing the risk of systemic side effects.
3. **Multiple Dosage Forms Offer Flexibility:** The availability of oral suspension, pastilles, and cream formulations allows for tailored treatment based on patient preferences and the specific characteristics of the infection.
4. **Relatively Inexpensive and Accessible:** Nystatin is a relatively inexpensive medication, making it accessible to a wide range of patients.
5. **Established Safety Profile:** Nystatin has a long history of safe and effective use in treating oral candidiasis, with minimal risk of serious side effects when used as directed.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Taste Can Be Unpleasant:** Some patients find the taste of Nystatin unpleasant, which can affect adherence to the treatment regimen.
2. **Requires Frequent Administration:** Nystatin typically needs to be administered several times a day, which can be inconvenient for some patients.
3. **May Not Be Effective Against Resistant Strains:** In some cases, *Candida* strains may be resistant to Nystatin, requiring alternative antifungal medications.
4. **Does Not Address Underlying Causes:** Nystatin only treats the fungal infection and does not address any underlying factors that may be contributing to the development of MRG, such as smoking, dentures, or immunocompromised status.
### Ideal User Profile
Nystatin is best suited for individuals with *Candida*-associated median rhomboid glossitis who are otherwise healthy and have no contraindications to the medication. It is particularly useful for patients with mild to moderate infections and those who prefer a topical treatment option with minimal systemic side effects. However, it may not be the best choice for individuals with severe infections, immunocompromised status, or known resistance to Nystatin.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly)
* **Fluconazole:** A systemic antifungal medication that is often used for more severe or resistant cases of oral candidiasis. Fluconazole is generally more effective than Nystatin, but it also carries a higher risk of systemic side effects.
* **Clotrimazole Troches:** Another topical antifungal medication that is available as a lozenge. Clotrimazole troches are often used as an alternative to Nystatin, particularly for patients who find the taste of Nystatin unpleasant.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Nystatin remains a valuable and effective treatment option for *Candida*-associated median rhomboid glossitis, particularly for mild to moderate infections. Its topical action minimizes the risk of systemic side effects, and its affordability makes it accessible to a wide range of patients. However, it’s essential to consider the potential for unpleasant taste, the need for frequent administration, and the possibility of resistant strains. For more severe or resistant infections, systemic antifungal medications like Fluconazole may be necessary. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual case.
## Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to median rhomboid glossitis:
1. **Q: Can median rhomboid glossitis be a sign of a more serious underlying health condition?**
**A:** While MRG itself is benign, it can sometimes be associated with underlying conditions like diabetes or immunosuppression. If you have MRG, it’s a good idea to discuss any other health concerns with your doctor.
2. **Q: How can I differentiate median rhomboid glossitis from oral cancer?**
**A:** MRG typically presents as a smooth, symmetrical, and painless lesion. Oral cancer lesions are often irregular, ulcerated, and may be painful. However, any suspicious oral lesion should be evaluated by a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis.
3. **Q: What are the risk factors for developing median rhomboid glossitis?**
**A:** Risk factors include smoking, denture wearing, steroid inhaler use, and conditions that weaken the immune system, such as diabetes or HIV.
4. **Q: Is median rhomboid glossitis contagious?**
**A:** No, median rhomboid glossitis itself is not contagious. However, if a fungal infection is involved, it’s important to practice good oral hygiene to prevent the spread of the fungus to other areas of the mouth or to other people.
5. **Q: Can I use over-the-counter antifungal medications to treat median rhomboid glossitis?**
**A:** While some over-the-counter antifungal medications may provide temporary relief, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and prescription-strength treatment.
6. **Q: How long does it take for median rhomboid glossitis to resolve with treatment?**
**A:** With appropriate treatment, most cases of *Candida*-associated MRG resolve within 2-4 weeks. However, recurrence is possible, especially if underlying risk factors are not addressed.
7. **Q: What are some lifestyle changes I can make to prevent median rhomboid glossitis?**
**A:** Quitting smoking, practicing good oral hygiene, properly cleaning dentures, and managing underlying health conditions can help prevent MRG.
8. **Q: Are there any home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms of median rhomboid glossitis?**
**A:** While home remedies may provide temporary relief, they are not a substitute for professional medical treatment. Saltwater rinses can help soothe the affected area, and avoiding irritating foods and beverages can also be beneficial.
9. **Q: If I have median rhomboid glossitis, do I need to see a specialist?**
**A:** In most cases, your general dentist or primary care physician can diagnose and treat MRG. However, if the condition is severe, recurrent, or unresponsive to treatment, a referral to an oral surgeon or dermatologist may be necessary.
10. **Q: Can median rhomboid glossitis affect my sense of taste?**
**A:** In some cases, MRG can affect the sense of taste, particularly if the taste buds in the affected area are damaged. However, this is usually temporary and resolves with treatment.
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
Median rhomboid glossitis, while often asymptomatic, requires careful attention to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. This comprehensive guide has provided an in-depth exploration of MRG, covering its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and potential complications. By understanding the role of fungal infections and other contributing factors, you can take proactive steps to maintain your oral health and prevent recurrence.
As we look to the future, research continues to refine our understanding of the oral microbiome and its impact on conditions like MRG. Staying informed about the latest advancements in diagnostic and treatment approaches is essential for both healthcare professionals and individuals seeking optimal oral health. We encourage you to share your experiences with median rhomboid glossitis in the comments below and explore our advanced guide to oral hygiene for more information on maintaining a healthy mouth. If you have concerns about median rhomboid glossitis, contact our experts for a consultation to discuss your specific needs and develop a personalized management plan.